Anhui Feichun Kabel Khusus Co., Ltd

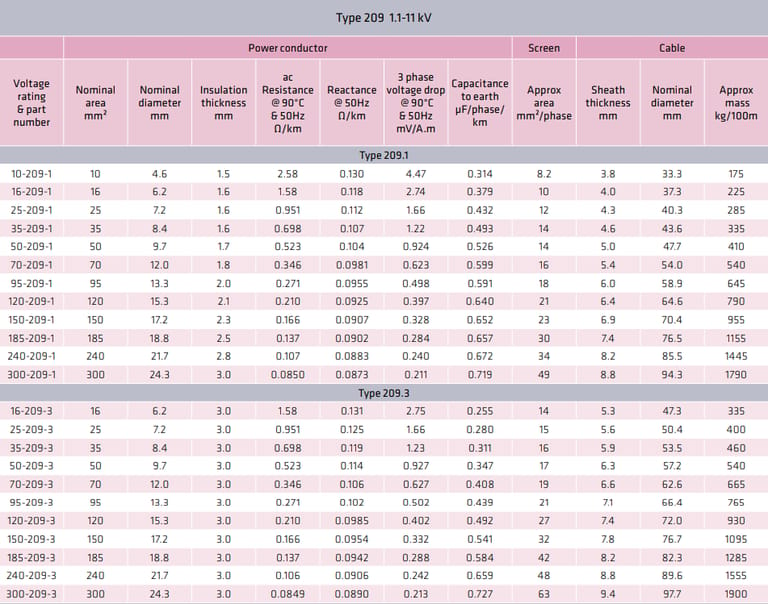
AS/NZS 1802 Type 209 1.1-11 kV
Cable description: Composite screened cable for general use to AS/NZS 1802.
Application: 1.1/1.1 kV to 11/11 kV general cable used extensively for feeder connection between transformer and gate-end box or similar, or feeder cables to pumps, fans, crushers, etc or as a substitute to Type A or B feeder cables. This cable can also be used above ground for power supply to mobile equipment.
Approvals: AS/NZS 1802 AS/NZS 1972 AS/NZS 5000.1
Temperature range: Maximum operating temperature: +90°C Minimum operating temperature: -25 °C
Flexibility: Flexible
Resistance to
Chemical exposure: Very good/Frequent
Mechanical impact: Heavy
Water exposure: Immersion/Temporary coverage
Solar radiation and
weather exposure: Suitable for direct exposure
Cable design
Composite screened cores with a single extensible pilot.
Core: Metal: tinned copper, three core plus central pilot.
Conductor separator tape: 1.1/1.1 kV – polyester. 3.3 kV and above – semiconductive tape.
Insulation: EPR (R-EP-90).
Insulation tape: 1.1/1.1 kV – proofed textile. 3.3 kV and above – semiconductive screen.
Screen: Composite screen (earth) of tinned annealed copper wire and polyester yarn.
Core colours: red, white, blue braid tracers.
Pilot: Single, in centre of cable.
Maximum DC resistance; 5.5 Ω/100 m for power cores to 35 mm². 3 Ω/100 m for power conductors above 35 mm².
Sheath: Heavy duty HD-85-PCP Sheath reinforcement is available upon request.
Installation conditions
In free air In duct Mobile equipment Machines
What Does “AS/NZS 1802 Type 209” Actually Mean?
What Is AS/NZS 1802 and Why Is It Important for Mining Cables?
AS/NZS 1802 is a specialised Australian/New Zealand standard that defines flexible reeling, trailing, and feeder cables specifically for mining and industrial applications. Unlike general industrial cable standards, AS/NZS 1802 focuses on:
Heavy mechanical duty
Enhanced earthing and screening
Flame retardancy
Electrical integrity under movement and vibration
Suitability for underground and surface mining hazards
In practice, a cable compliant with AS/NZS 1802 is engineered for continuous abuse, not just electrical performance.
What Makes Type 209 Different from Other AS/NZS 1802 Cable Types?
Within AS/NZS 1802, different cable “types” define construction philosophy and application scope. Type 209 occupies a critical position as a composite screened medium-voltage feeder cable, offering:
Higher safety than unscreened Type A feeders
Greater flexibility than rigid MV power cables
Built-in pilot for earth continuity monitoring
Suitability as a substitute for Type A or Type B feeder cables
This balance explains why Type 209 is often selected as a standardised feeder solution in modern mines.
How Is AS/NZS 1802 Type 209 Cable Designed?
What Is a Composite Screened Mining Cable?
A composite screened cable combines earthing and screening functions into a single integrated layer, rather than using separate metallic screens or armour. In Type 209, this composite screen:
Maintains earth continuity
Controls electrical stress
Enhances fault detection
Improves flexibility compared with metallic armour
This design is especially valuable in underground mines, where cable movement, abrasion, and confined installation spaces are unavoidable.
What Are the Electrical and Technical Specifications of Type 209?
What Voltage Ratings Are Available?
AS/NZS 1802 Type 209 mining cable is available in:
1.1/1.1 kV (Type 209.1)
3.3/3.3 kV (Type 209.3)
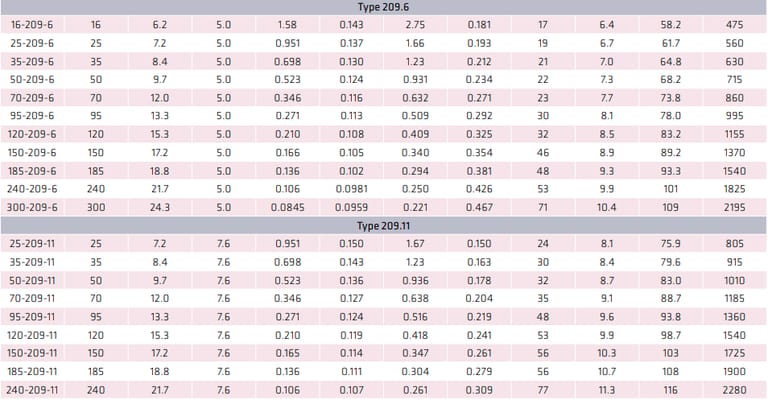
6.6/6.6 kV (Type 209.6)
11/11 kV (Type 209.11)
Each voltage class features increased insulation thickness and enhanced stress control.
What Conductor Sizes Are Commonly Used?
Standard conductor sizes range from 16 mm² to 300 mm², allowing engineers to balance:
Load current
Feeder length
Voltage drop limits
Mechanical robustness
Large platinum mines in Limpopo, for example, frequently use 120–240 mm² Type 209.6 cables for long underground feeders.
How Do Resistance, Reactance, and Voltage Drop Affect Selection?
Key electrical parameters include:
AC resistance @ 90 °C
Reactance @ 50 Hz
Three-phase voltage drop (mV/A·m)
Proper selection ensures motors start reliably, protection systems operate correctly, and energy losses are minimised—particularly important for long feeder runs.
How Do Type 209 Variants Differ?
What Is the Difference Between Type 209.1, 209.3, 209.6, and 209.11?
Variant | Voltage | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
209.1 | 1.1 kV | Low-voltage feeders, auxiliaries |
209.3 | 3.3 kV | Medium pumps, fans |
209.6 | 6.6 kV | Crushers, conveyors |
209.11 | 11 kV | Long-distance MV feeders |
Higher voltages mean thicker insulation, lower capacitance per unit power, and improved transmission efficiency.
Where Is AS/NZS 1802 Type 209 Commonly Used?
Why Is Type 209 Ideal for Underground Mining?
Type 209 is widely used for:
Transformer-to-gate-end box feeders
Power supply to pumps and ventilation fans
Crushers and conveyor drives
Can Type 209 Be Used Above Ground?
Yes. Thanks to its UV-resistant PCP sheath, Type 209 is commonly used:
On surface mobile equipment
Between substations and processing plants
In open-cast mining operations
How Does Type 209 Perform in Harsh Conditions?
Type 209 demonstrates excellent resistance to:
Mechanical impact from falling rock
Chemical exposure from oils and mine water
Temporary water immersion and flooding
This makes it suitable for high-risk zones where cable damage would otherwise be frequent.
Kabel Pertambangan Feichun
Kabel pertambangan yang tahan lama untuk lingkungan dan operasi yang berat
Alamat Email
© 2025. All rights reserved.


Produk
Kabel Tambang AS/NZS
Kabel Tambang DIN VDE
Kabel Tambang BS 6708
Kabel Tambang ICEA & CAN/CSA
Kabel Berselubung Baja
Kabel Gulung / Kabel Reeling
Kabel Festoon / Kabel Rel Kren
Perusahaan
Kontak
WhatsApp: +86 17333223430
Social Media:
